Space Economy: Advancements in Space Science and Missions
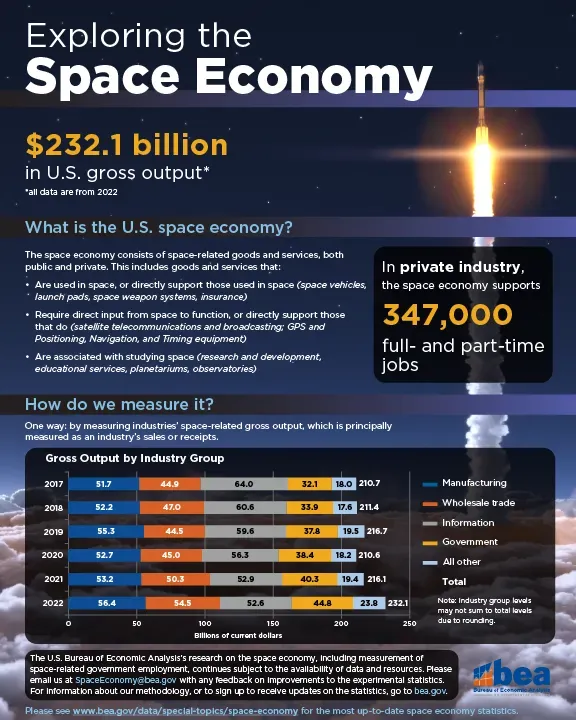
The space economy is experiencing a remarkable transformation, igniting a new era in space science and exploration. With investments exceeding half a trillion dollars in 2023, this dynamic market is largely fueled by private space funding, which has outpaced traditional public investments for the first time. The rise of the new space economy is reshaping how we approach space missions, making them more accessible and cost-efficient. As space technology innovation accelerates, it encourages a competitive landscape that drives down costs and enhances the quality of our ventures into the cosmos. Ultimately, the intersection of robust financial backing and advanced technological capabilities promises a future rich with possibilities in space science.
The commercial space sector, often referred to as the new frontier of exploration, is redefining the landscape of aerospace activities. With a surge in private sector involvement, this burgeoning field is not only emphasizing economic growth but also pushing the envelope of space technology innovation. As private enterprises invest heavily in ambitious space missions, they are catalyzing a shift in how we perceive and engage with the universe. This evolution in the space marketplace brings forth unique business models and funding strategies, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements. As we explore these developments, it becomes crucial to understand how this fresh approach will benefit scientific endeavors and foster more ambitious projects in astrobiology and beyond.
The Rise of the New Space Economy
In recent years, the concept of the new space economy has transformed how we perceive and conduct space missions. With private investments surpassing public funding in 2023, an unprecedented wave of financial support has emerged, allowing commercial entities to take the lead in space exploration and technology innovation. This shift has created a dynamic marketplace where competition flourishes, subsequently driving down the costs of launches and operations. As we witness this evolution, it’s crucial to evaluate how these changes impact not just commercial endeavors but also large-scale scientific missions.
The implications of a thriving new space economy extend far beyond mere financial aspects; they introduce a paradigm shift in the way space capabilities are developed and utilized. With a move towards vertical integration and service-oriented business models, private companies can streamline operations and reduce redundancy. As costs decrease, opportunities for significant scientific endeavors like those achieved by the Hubble Space Telescope or the James Webb Space Telescope become more attainable. This environment promotes innovation and collaboration, creating pathways for groundbreaking missions that can advance our understanding of the universe.
Unlocking Space Science Through Innovation
To fully harness the potential of the new space economy, the scientific community must embrace innovation across multiple dimensions. The pillars of this economy—technology, business, and cultural innovation—must be integrated into the planning and execution of space missions. For instance, technology innovation can lead to both incremental and disruptive advancements, enabling scientists to utilize new tools and methodologies that enhance their research capabilities. This can dramatically improve the efficiency of mission designs and the quality of scientific data collected.
Business innovation is another crucial component. By adapting to service-oriented models and focusing on scalable production, organizations can better manage project risks and costs. Cultural innovation encourages a willingness to experiment and adapt to new ideas, promoting iterative development processes that can lead to significant breakthroughs. When the scientific community aligns with these innovative frameworks, they can leverage funding from private sectors to conduct ambitious scientific missions, ultimately transforming our approach to space exploration and research.
Cost Reduction in Space Missions
As the space economy evolves, one of the most significant benefits is the reduction in costs associated with launching and conducting space missions. Historically, missions like those of HST and JWST came with hefty price tags, often limiting the frequency and scale of exploratory endeavors. However, with the advent of private financing and competitive markets, the landscape has shifted. Companies are striving to offer low-cost launch options, which not only democratizes access to space but also allows scientific teams to focus on groundbreaking research without the burden of astronomical expenses.
The emphasis on cost reduction is not merely about spending less; it’s about reallocating resources strategically to maximize scientific output. For example, lower launch costs mean that scientific teams can propose more daring missions that were once considered financially unfeasible. This opens doors to exploring more celestial bodies, conducting more comprehensive research, and ultimately enhancing our understanding of fundamental space science principles. As the new space economy continues to thrive, researchers stand at the forefront of an unprecedented opportunity.
Private Space Funding and Its Impact
The rise of private space funding has created a new ecosystem for both commercial and scientific initiatives in space exploration. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have demonstrated that with enough financial support, sophisticated space technologies can be developed and implemented at a fraction of the cost of government programs. This influx of capital has been crucial for fostering innovation within the field, enabling a range of projects from satellite deployment to interplanetary missions.
Moreover, private funding has also acted as a catalyst for collaboration between public institutions and commercial entities. Public agencies like NASA are increasingly looking to private partners to share costs and resources in conducting ambitious space missions. This synergy not only enhances the scope and scale of research initiatives but also paves the way for a more resilient space economy capable of adapting to future challenges. As we look ahead, the relationship between private interests and governmental space endeavors will be pivotal in shaping the future of space exploration.
Space Technology Innovations Transforming Research
Innovations in space technology have been a game changer for the field of space science. Advances such as more efficient propulsion systems, miniaturized satellites, and improved data transmission methods are revolutionizing the way we conduct research in space. These developments allow for the execution of more complex missions with greater precision and shorter timelines. For instance, the use of CubeSats has significantly lowered barriers for research projects, enabling a wide array of scientific experiments previously deemed overly ambitious.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in data analysis has transformed how scientists process and interpret vast amounts of data captured from space missions. This innovative approach ensures that valuable information is not only collected but also utilized effectively, leading to timely and relevant findings in space science. As these technological advancements continue to unfold, they expand the possibilities for future research, yielding insights that could reshape our understanding of the universe.
Challenges in Implementing Effective Space Missions
While the new space economy presents numerous opportunities, it also introduces challenges that need addressing to ensure effective space missions. The reliance on private funding can lead to shifts in project priorities based on commercial viability over scientific value. As a result, there is a risk that long-term scientific goals may be overshadowed by short-term profit motives. This creates a pressing need for robust frameworks that balance both commercial interests and the imperatives of scientific discovery.
Furthermore, navigating the regulatory landscape of space can be complex. With multiple stakeholders, including governments, private companies, and international bodies involved, coordination can become cumbersome. Efficient communication and agreement on shared goals are essential to overcoming these barriers. Emphasizing collaboration among all parties involved will be critical in sustaining an environment where both innovative space ventures and crucial science can thrive harmoniously.
Cultural Shifts Towards Space Exploration
The cultural perception of space exploration is undergoing a significant transformation, largely driven by the rise of the new space economy and public fascination with commercial spaceflight. This shift is encouraging a broader audience to engage with space science and technology. As private companies launch missions that attract public attention—such as space tourism and live-streamed launches—there is a growing awareness of the scientific endeavors that accompany these projects.
Education and outreach efforts are also changing, as more people are inspired to explore careers in STEM fields related to space science. Such developments are paramount for nurturing future generations of scientists and engineers. By fostering a culture that celebrates space exploration, society can cultivate a workforce that is prepared to tackle the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the ever-expanding realm of the cosmos.
The Future of Space Missions: Aspirations and Realities
The future of space missions is a blend of ambition and pragmatism, characterized by the aspirations of both governmental agencies and private enterprises. As our capabilities grow, expectations naturally increase. The potential for more frequent and varied missions will depend on how well we can leverage the advantages presented by the new space economy while remaining grounded in scientific integrity and purpose.
Looking forward, strategic partnerships between public and private sectors will be essential in realizing the lofty goals set for future exploration. As technology progresses and costs decrease, exciting prospects emerge for returning samples from Mars, exploring distant exoplanets, or searching for signs of life in our solar system. However, to achieve these ambitious missions, a collaborative and innovative framework will be vital, ensuring that both the wonders of space science and the economic benefits are realized.
Frequently Asked Questions
What impact does the new space economy have on space science funding?
The new space economy significantly enhances funding for space science by attracting private investments that now exceed public funding. This shift allows for more ambitious space missions and innovative technologies, fostering faster development at reduced costs.
How does technology innovation contribute to the space economy?
Technology innovation is a crucial part of the space economy, enabling both incremental and disruptive advancements. This innovation leads to more efficient space technology, lowering costs for launching and supporting complex space missions.
What are the benefits of private space funding for space missions?
Private space funding offers several benefits for space missions, including increased competition that drives costs down, faster project timelines, and more flexible approaches to mission design. This growing investment from the private sector complements traditional funding sources and expands mission possibilities.
How can cultural innovation drive success in the new space economy?
Cultural innovation encourages openness to risk and iterative development in the new space economy. This mindset allows organizations to experiment with new ideas and approaches, ultimately leading to breakthroughs in space technology and more effective space missions.
What role does business innovation play in supporting the space economy?
Business innovation, such as vertical integration and service-oriented models, enhances the efficiency and scalability of space operations. This innovation results in lower costs and increased access to space, making complex science missions more feasible.
Why is it essential for the scientific community to engage with the new space economy?
Engaging with the new space economy is essential for the scientific community because it opens up new funding streams and partnerships, allowing for groundbreaking space science missions that would have been financially out of reach through traditional funding mechanisms alone.
Can the new space economy help reduce the costs of launching missions like HST and JWST?
Yes, the new space economy can reduce the costs of launching missions similar to HST and JWST. By leveraging innovation, competitive markets, and private investment, the scientific community can achieve high-quality and cost-effective space missions.
What challenges does the new space economy face in supporting space science?
Challenges include ensuring consistent funding streams, balancing commercial interests with scientific goals, and fostering collaboration between public and private sectors to optimize resource use for fulfilling ambitious space science objectives.
How does the space economy influence the future of space technology innovation?
The space economy fosters an environment where rapid technological advancements are prioritized, leading to innovative solutions that enhance mission capabilities, improve safety, and significantly reduce operational costs.
What future developments can we expect from the connection between space science and the new space economy?
Future developments may include more collaborative efforts between scientists and private companies, enhanced capabilities for deep space exploration, and increased accessibility to space for research, all driven by the growing momentum of the new space economy.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Investment Growth | Monetary investments in space exceeded half a trillion dollars in 2023. |
| Rise of the New Space Economy | Private commercial funding surpassed public investments for the first time last year. |
| Cost Reduction | Competition from the new space economy has led to dramatic reductions in costs and schedules for space missions. |
| Three Pillars of Innovation | 1. Technology innovation through incremental and disruptive innovations. 2. Business innovation via vertical integration and service-oriented models. 3. Cultural innovation embracing risk and iterative development. |
| Future of Space Science | The integration of these innovations could enable powerful missions in basic science like HST, Chandra, and JWST. |
Summary
The space economy is rapidly evolving, presenting numerous opportunities for scientific advancement. With significant investments and a shift towards private funding, the potential for conducting ambitious scientific missions has never been greater. Embracing technological, business, and cultural innovations will be essential for the scientific community to capitalize on the benefits of the new space economy and elevate space exploration to new heights.