Geopolitical Risks: Implications for Financial Stability
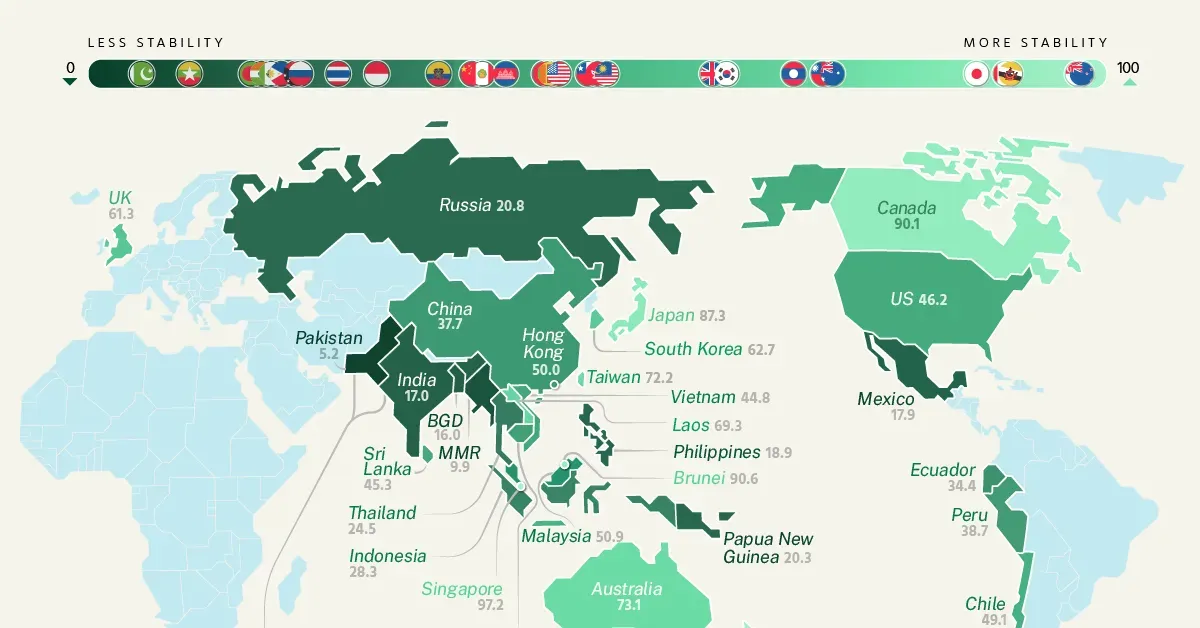
Geopolitical risks are increasingly becoming a focal point for investors and analysts alike, as their implications stretch far beyond local borders. These risks, which include military conflicts and diplomatic tensions, can significantly impact financial stability and asset prices on a global scale. In particular, emerging markets are often the most vulnerable, facing heightened market volatility and rising sovereign risk premiums in response to geopolitical events. As these risks materialize, they can disrupt trade flows and financial linkages, fostering an environment of uncertainty that further affects investor confidence. Understanding and managing geopolitical risks is crucial for maintaining market equilibrium and ensuring robust financial systems in an interconnected world.
When discussing geopolitical uncertainties, terms such as international tensions or political instability often emerge. These elements play a critical role in shaping the landscape of global finance, particularly in relation to market dynamics and investment outcomes. The effects of such uncertainties can lead to fluctuations in asset valuations and influence overall economic resilience. Additionally, risk premiums associated with sovereign debt may rise as investors perceive higher levels of financial instability. Therefore, navigating these complex dimensions requires a keen awareness of the interrelations between political events and financial market reactions.
Understanding Geopolitical Risks and Their Impact
Geopolitical risks refer to the potential for instability or conflict in a region that can negatively affect economies and financial markets. Investors are increasingly aware of these risks and, as a result, they often factor them into their investment decisions. However, the actual implications of geopolitical events can be more significant than initially anticipated. For instance, while minor conflicts may only cause short-term fluctuations in asset prices, major events like military interventions can lead to substantial and prolonged downturns in the equity markets.
In emerging markets, the influence of geopolitical risks is particularly pronounced due to their vulnerability to external shocks. Countries with lower fiscal buffers or limited international reserves tend to experience heightened market volatility in response to geopolitical tensions. Higher sovereign risk premiums often accompany these events, reflecting the increased costs of borrowing and the perceived risk of investing in these regions. Therefore, understanding the implications of geopolitical risks is crucial for maintaining financial stability, especially in areas with burgeoning but fragile economies.
The Role of Asset Prices in Reflecting Geopolitical Risks
Asset prices function as a barometer for market sentiment regarding geopolitical events. When tensions escalate, investors often retreat to safer assets, leading to a reallocation of capital that can depress stock prices significantly, particularly in geopolitically sensitive sectors. This shift not only affects individual stocks but can also impact broader market indices. For instance, companies with significant exposure to politically unstable regions may see their stock prices decline disproportionately.
Moreover, the relationship between asset prices and geopolitical risks is not straightforward; it often interacts with market expectations and investor behavior. As geopolitical tensions simmer, premiums on sovereign debt may rise, reflecting worries about potential defaults or economic slowdown. This volatility can create a feedback loop, where declining asset prices exacerbate financial instability, leading to tighter credit conditions and a less resilient economy overall.
Mitigating Financial Instability through Risk Management
To safeguard against the financial instability that can ensue from geopolitical risks, financial institutions must proactively manage these threats. This can be achieved by implementing comprehensive risk management frameworks that incorporate stress testing and scenario analysis. By simulating various geopolitical scenarios, institutions can better understand potential vulnerabilities and prepare appropriate responses to minimize market disruptions.
Furthermore, emerging markets, in particular, should focus on enhancing their financial infrastructures. This includes developing deeper capital markets and ensuring sound fiscal policies that can withstand external shocks. By maintaining adequate reserves and promoting resilient financial systems, these economies can mitigate the adverse impacts of geopolitical events, safeguarding their financial stability and investor confidence.
Investors’ Perception of Geopolitical Risks
Investors play a crucial role in shaping the financial landscape, and their perception of geopolitical risks can lead to significant market reactions. When investors anticipate geopolitical conflicts, they often adopt a more cautious approach, which can lead to increased market volatility. For example, during periods of heightened tensions, investors may sell off risky assets, opting for safer options like bonds or gold, causing fluctuations in asset prices across various sectors.
The interplay between investor sentiment and geopolitical developments can create a cycle of volatility where fear of instability drives down asset prices, only to be followed by periods of recovery once tensions ease. Understanding this cycle is essential for investors as they navigate the unpredictable nature of the global markets, particularly those involving emerging economies under the shadow of geopolitical risks.
The Interconnectedness of Global Markets and Geopolitical Events
Globalization has led to greater interconnectedness among financial markets, meaning that geopolitical events in one region can have far-reaching effects on others. For instance, a conflict in a resource-rich country can lead to spikes in commodity prices, influencing inflation rates and economic stability in distant markets. This interconnectedness necessitates a comprehensive approach to assessing geopolitical risks, as their impacts transcend borders.
Investors need to recognize that geopolitical risks can transmit through various channels—trade networks, asset price correlations, and financial flows. Thus, a geopolitical event that initially appears localized can quickly escalate to affect global markets, highlighting the importance of international cooperation and comprehensive risk assessment strategies among financial institutions across nations to maintain stability.
The Long-term Implications of Geopolitical Risk Events
The long-term implications of geopolitical risk events extend beyond immediate market reactions and can have lasting effects on financial stability. For example, prolonged periods of heightened geopolitical tension can lead to structural changes in global trade patterns, as countries seek to minimize their exposure to risk-prone regions. This shift may result in a reallocation of investment strategies and a reevaluation of asset prices in the long run.
Moreover, the fallout from geopolitical events can necessitate changes in sovereign policies, as governments strive to strengthen their resilience against future shocks. Countries may implement reforms aimed at boosting financial stability, which in turn can influence investor confidence and leading to changes in risk premiums across different markets. Understanding the long-term impacts of these risks is essential for stakeholders looking to navigate the evolving landscape of global finance.
Emerging Markets: A Case Study on Geopolitical Risks
Emerging markets present a unique case regarding how geopolitical risks influence financial stability. These regions often have more pronounced vulnerabilities due to less developed financial systems and limited fiscal capacities. Therefore, geopolitical tensions can lead to significant movements in sovereign risk premiums, reflecting the market’s perception of heightened risk. For example, during times of political unrest, emerging markets may experience sharp declines in asset prices as investors flee to safer investments.
To counter these challenges, emerging economies must enhance their institutional frameworks and engage in better risk management practices. This might involve strengthening regional cooperation and establishing mechanisms for mutual support during geopolitical crises. By doing so, emerging markets can cultivate a more robust economic environment, reducing the adverse effects of external shocks arising from geopolitical risks, and ultimately promoting long-term financial stability.
Proactive Strategies for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions play a vital role in mitigating the risks associated with geopolitical events. Proactive strategies such as diversification of asset portfolios, investment in risk management technologies, and continuous monitoring of geopolitical developments are essential for minimizing market exposure. By being vigilant and prepared, institutions can better navigate the complexities posed by unexpected geopolitical events.
Additionally, financial institutions should foster collaborative relationships with regulatory bodies to enhance the effectiveness of risk management practices. By sharing insights and developing frameworks capable of adapting to the dynamic landscape of geopolitical risks, these entities can contribute significantly to preserving financial stability across markets.
Conclusion: Preparing for Uncertainty in Geopolitical Landscapes
As geopolitical landscapes evolve and uncertainties become more pronounced, the need for adaptive strategies in financial markets becomes critical. Stakeholders must remain vigilant and responsive to geopolitical risks that could threaten asset prices and overall financial stability. By implementing sound risk management frameworks and maintaining clear communication with investors, financial institutions can mitigate potential fallout from geopolitical events.
In conclusion, while geopolitical risks are inherent in global finance, proactive measures can help institutions and investors alike weather the storms these risks present. By fostering an environment of resilience and preparedness, stakeholders can maintain confidence in their markets, ensuring stability amid an increasingly interconnected and unpredictable world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of geopolitical risks on financial stability?
Geopolitical risks can impact financial stability by affecting asset prices and increasing market volatility. Significant geopolitical events, like military conflicts, often lead to declines in stock prices and increased sovereign risk premiums, particularly in emerging markets with limited fiscal capacity.
How do geopolitical risks affect asset prices in emerging markets?
In emerging markets, geopolitical risks can lead to heightened uncertainty, resulting in greater asset price fluctuations. Limited fiscal space and international reserves make these economies more vulnerable to adverse shocks, causing investors to reassess risk and adjust asset valuations accordingly.
What is the relationship between geopolitical risks and market volatility?
Geopolitical risks are linked to market volatility, as their sudden realization can create uncertainty in financial markets. When investors react to geopolitical events, it often results in sharp movements in asset prices and heightened volatility, particularly in equities and foreign exchange markets.
How do sovereign risk premiums relate to geopolitical risks?
Sovereign risk premiums tend to rise in response to geopolitical risks as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the increased likelihood of default or instability in affected countries. This premium reflects the perceived risk of investing in nations experiencing significant geopolitical tensions.
What measures can financial institutions take to mitigate risks from geopolitical events?
Financial institutions can better manage geopolitical risks by allocating resources towards identifying and quantifying these events, conducting stress tests, and engaging in scenario analysis. This proactive approach helps institutions prepare for potential financial stability challenges arising from geopolitical developments.
Why are geopolitical risks particularly concerning for emerging markets?
Emerging markets often face greater challenges from geopolitical risks due to their limited fiscal capabilities and lower international reserves. When geopolitical tensions arise, these factors can exacerbate financial instability, leading to significant impacts on asset prices and overall economic health.
How can developing economies bolster their resilience against geopolitical risks?
Developing economies can enhance resilience against geopolitical risks by strengthening their financial markets, maintaining prudent fiscal policies, and ensuring adequate international reserves. These measures help cushion their economies against adverse shocks, thus promoting greater financial stability.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Geopolitical Risks Influence Asset Prices | Generally modest but can lead to significant declines during major events. |
| Impact on Emerging Markets | More pronounced in countries with limited fiscal space or reserve buffers. |
| Propagation through Trade | Risks can spread to other nations via trade and financial links. |
| Market Volatility | Investors price some geopolitical risks, but major events can trigger volatility. |
| Risks to Financial Institutions | Major events may impact stability of banks and financial systems. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Financial institutions should adopt stress testing and scenario analysis. |
| Development in Emerging Markets | Need for stronger financial markets and fiscal policies to buffer against shocks. |
Summary
Geopolitical risks are a critical factor impacting global financial stability, influencing asset prices significantly, especially during major events like military conflicts. Understanding these risks is essential for investors and financial institutions alike, as they can lead to increased market volatility and potential risks to the stability of banking and financial systems. Institutions need to take proactive measures to identify and manage these risks effectively, while emerging markets must bolster their financial frameworks to mitigate the adverse effects of geopolitical shocks.




